Climate change & environmental quality
Reducing emissions and improving the system’s resiliency
While climate change is a global phenomenon, a number of its impacts are showing up here in Minnesota. For example, the annual average temperature in Minnesota has risen two degrees over the past century — that's 25 percent more than the global average. It's even greater in the northern part of the state, where the average temperature has risen three degrees over the past 100 years. Most of the increase has been in the winter and is seen in higher low-temperatures rather than warmer high-temperatures. In addition to warmer winters, Minnesota has experienced more large storms in recent decades. More and more of Minnesota’s rainfall is occurring as heavy rain events.
Both warmer winters and changes in the type of rain events affect the transportation system in Minnesota. The chart below identifies what these effects. It also highlights other potential climate impacts and how confident we are that Minnesota will see a change in these impacts over the next 20 years. Given the potential effects of the transportation system, it’s important for MnDOT and other transportation partners in Minnesota to track climate trends, understand where the system is vulnerable, and plan for changes.
| Climate Change Impact | Likelihood this will change in MN over next 20 years | Implications for the Transportation System |
| Heavy precipitation / flooding | Very High |
|
| Warmer winters | Very High |
|
| New species ranges | High |
|
| Drought | Medium |
|
| High heat | Low |
|
| Wildfires | Unknown |
|
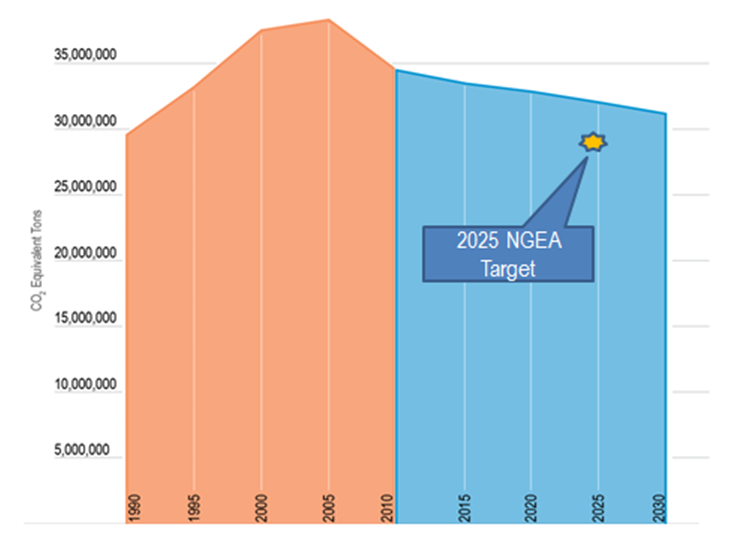
In addition to addressing the effects of climate change on the transportation system, MnDOT and other transportation partners also have to consider the ways in which transportation impacts the environment. For example, emissions from transportation impact air quality and can lead to broader health and environmental concerns. Through Minnesota's Next Generation Energy Act — passed in 2007 — Minnesota has a goal of decreasing greenhouse gas emission by 80 percent from 2005 levels by 2050, with benchmark targets for 2015 and 2025. While this goal is not specific to transportation, this update to the Statewide Multimodal Transportation Plan is proposing that MnDOT adopt these targets for the transportation sector to help ensure transportation does its part. Currently, transportation emissions in Minnesota are trending down but not fast enough to meet proposed targets.
Emissions are not the only way in which transportation impacts the environment. Other environmental challenges include the impacts of salt use and runoff on water quality as well as how roadside vegetation management affects pollinator populations, species habitat, and the spread of invasive species and noxious weeds.
What do you think? Let us know your thoughts belowin the right-hand sidebar at the top of this page.
